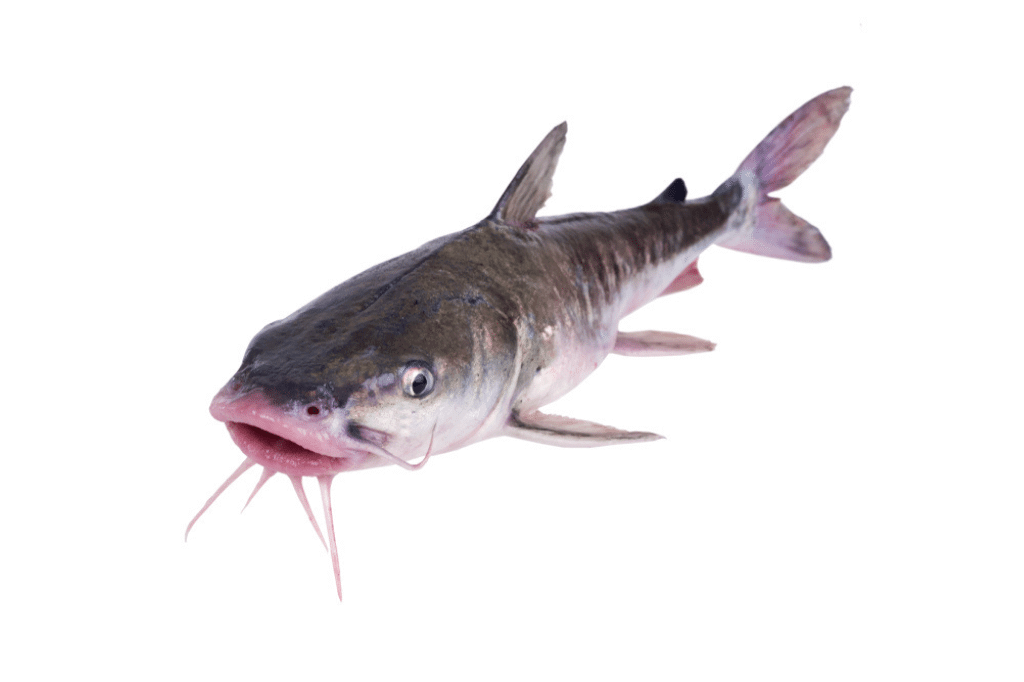
These hardy creatures inhabit a variety of brackish and saltwater areas, often thriving in murky waters where they can find an abundance of food. Saltwater catfish species, such as the Hardhead and Gafftopsail catfish, are common in the waters of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of the United States.
They play a significant role in the ecosystem as both predators and prey. Anglers sometimes catch these fish for sport or consumption, despite their reputation for being less desirable than their freshwater cousins. Their unique adaptations, like the ability to tolerate varying salinities, make saltwater catfish an intriguing subject for both fishermen and marine biologists.
Habitat
Marine Environments
Saltwater catfish prefer warm, shallow waters, often found in estuaries, bays, and coastal areas. These environments offer abundant food sources, including smaller fish and crustaceans.- Mangroves: Act as nurseries for juvenile catfish.
- Seagrass beds: Provide hiding spots and feeding grounds.
- Reef areas: Older catfish may venture here for food.
Distribution
Saltwater catfish have a wide geographic range that extends across various continents. They are prolific in the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico.| Region | Common Species |
|---|---|
| North America | Hardhead and gafftopsail catfish |
| South America | Ariidae family species |
| Australia | Fork-tailed catfish |
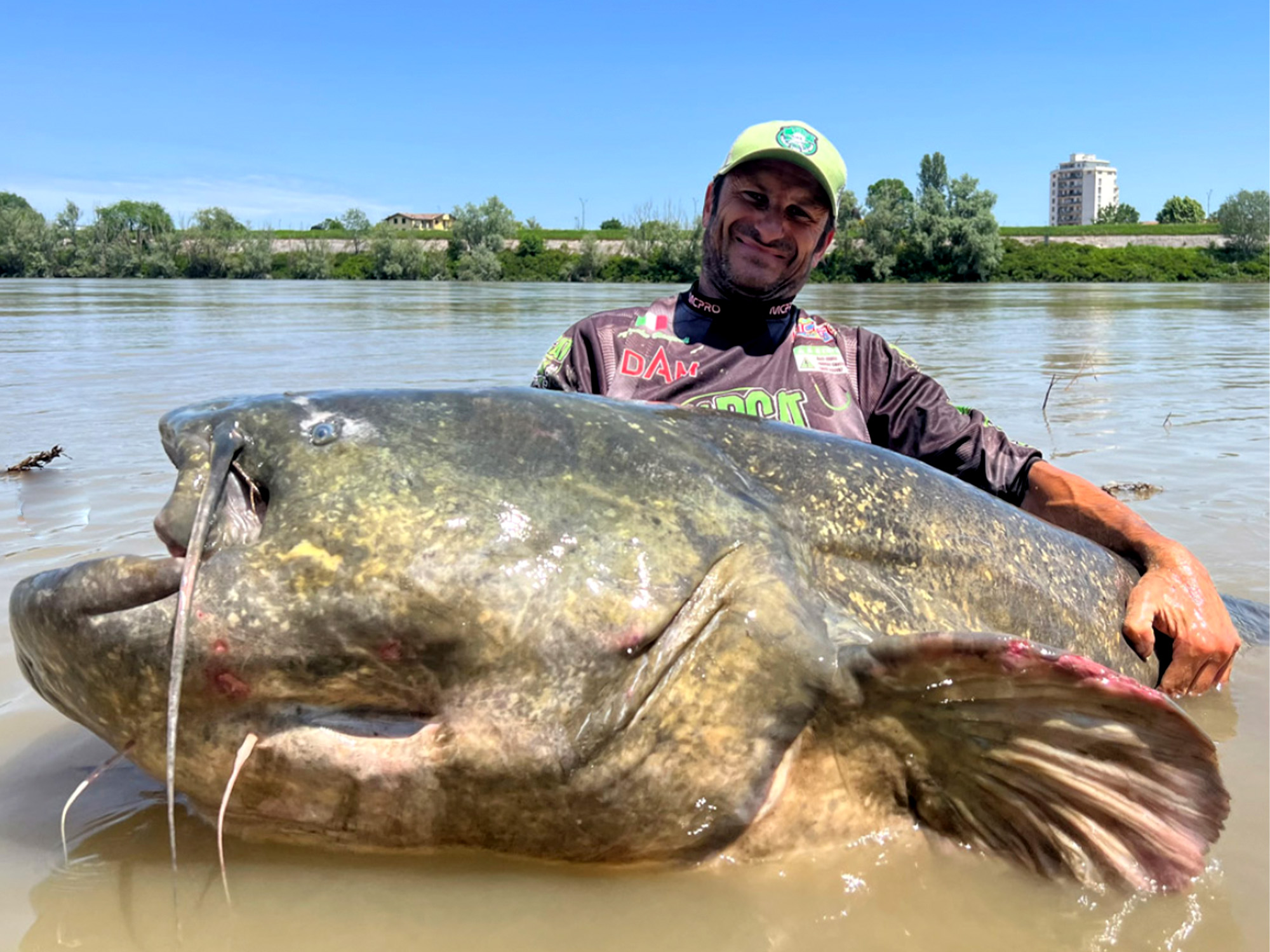

Behavior
Feeding Habits
Saltwater catfish have fascinating feeding patterns that help them survive. They primarily feed at dusk or during the night. They use their sensitive barbels to locate prey in murky waters.- Eat small fish, crustaceans, and plants.
- Search for food both at the bottom and mid-water levels.
- Exhibit a lie-and-wait strategy or actively forage for food.
Reproduction
The breeding behavior of saltwater catfish is quite intriguing. Mating season varies by location but often follows warm water patterns.- Females lay large amounts of eggs.
- Males guard and aerate the eggs until they hatch.
Adaptations
Osmoregulation
Saltwater catfish showcase a remarkable mastery of osmoregulation. This is their ability to maintain internal salt and water balance. Unlike freshwater species, they live in salt-heavy environments that could dehydrate other fish.- Specialized cells called chloride cells work to expel excess salt.
- Their kidneys play a vital role, ensuring the right concentration of urine to conserve water.
- Intake of water happens through their food and gills.
Physical Features
Saltwater catfish come with distinct physical characteristics. These traits are hand-in-glove fits for survival in their salty, sometimes murky homes.| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Barbels | Help in finding food in dark or muddy waters |
| Skin | Lacks scales, covered in mucus to minimize water loss |
| Fins | Adapted for steady swimming and quick bursts |

Importance
Ecological Role
Saltwater catfish are more than just fish; they’re vital to the ocean’s health. These fish act as both predator and prey in their habitats. Below are key points about their ecological role:- Bottom feeders: They clean the seabed by eating dead matter.
- Food resource: Larger fish, birds, and humans rely on them for food.
- Balance populations: By eating other species, they keep numbers in check.
Commercial Value
Saltwater catfish offer economic benefits. They are a popular choice for seafood lovers.| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Markets | They are sold fresh, frozen, or as specialty dishes. |
| Jobs | Fishing for these catfish provides livelihoods to many. |
| Cuisine | They feature in diverse culinary traditions worldwide. |
Threats
Pollution Impact
Our oceans suffocate under the grip of pollution. Saltwater catfish encounter this reality daily. Waters dense with pollutants turn their homes toxic. These conditions are unfit for their survival.- Trash: Discarded waste, plastic bags, and bottle caps threaten catfish habitats.
- Toxins: Industrial runoffs infuse the waters with deadly chemicals.
- Oil spills: Catastrophic events coat their environment, harming their delicate gills and skin.
Over fishing
Human appetites crave the bounty of the sea, often to its detriment. Over fishing looms over saltwater catfish populations. It disrupts their life cycles and can deplete their numbers rapidly.| Impact | Consequence |
|---|---|
| By catch: | Catfish caught unintentionally in nets may not survive. |
| Habitat destruction: | The endless pursuit for fish disrupts seabeds, crucial for catfish survival. |
Conservation Efforts
Protected Areas
Creating sanctuaries for saltwater catfish helps maintain their populations. These special zones, off-limits to fishing and other harmful activities, provide a safe haven. Projects are in place globally to expand these vital spaces.- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
- No-Take Zones (NTZs)
- Marine Reserves
Sustainable Fishing Practices
Sustainable fishing means catching fish without harming future generations. For saltwater catfish, this is critical. Rules are in place to ensure their protection.| Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Bycatch Reduction Devices | Save juveniles and non-target species |
| Seasonal Closures | Allow breeding without human interference |
| Quota Systems | Limit the number of catches |
Frequently Asked Questions On Saltwater Catfish
What Is The Difference Between Saltwater Catfish And Freshwater Catfish?
Saltwater catfish inhabit marine environments, are often hardier, and can handle higher salinity levels. Freshwater catfish thrive in rivers and lakes, requiring less saline conditions. Each type has adapted to its specific habitat’s water chemistry and ecosystem.
What Kind Of Saltwater Fish Looks Like A Catfish?
The marine fish resembling a catfish is the Gafftopsail Catfish (Bagre marinus). It features barbels and a flattened head similar to freshwater catfish.
How To Cook Saltwater Catfish?
Begin by cleaning the saltwater catfish, removing skin and fillets. Preheat the grill to medium-high. Season the fillets with your preferred spices. Grill each side for 3-5 minutes until the meat flakes easily. Serve immediately for best flavor.
How Do You Handle Saltwater Catfish?
Handle saltwater catfish with caution due to their venomous spines. Use gloves, grasp firmly behind the head, and avoid the sharp dorsal and pectoral fins. Release quickly and gently back into the water.
Conclusion
Exploring the realm of saltwater catfish offers fascinating insights. This resilient species adapts to diverse marine environments. Enthusiasts and anglers alike appreciate their unique traits. Remember, responsible practices ensure their populations thrive. Embrace the wonder of these captivating creatures of the sea.